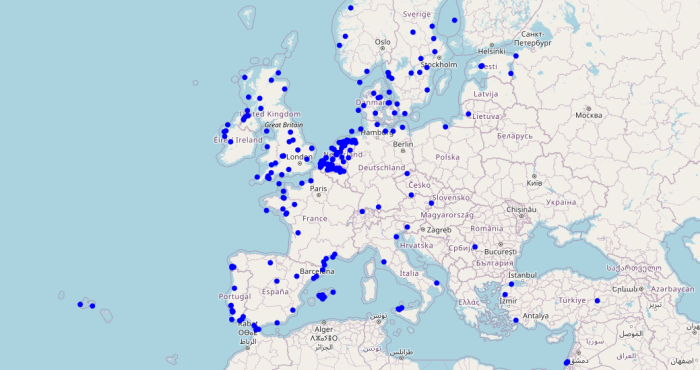
The LifeWatch Wallonia-Brussels team publishes their ecotope database of the Walloon region
This prototype of object-based landscape description provides more than 80 biotic and abiotic variables for functionally homogeneous landscape units. Online navigation tools help you navigate through the integrated information layers and the database is available for ecological modelers.
In the framework of LifeWatch, the Wallonia-Brussels Federation is financing a research program as a partnership between the Earth and Life Institute (UCL) and the Unit for Biodiversity and Landscape (Ulg-Gbx). The LifeWatch Wallonia-Brussels (LW-WB) team combines a strong experience in land cover mapping through with biodiversity modeling expertise.
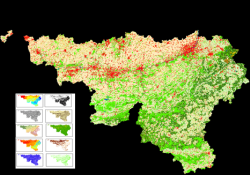
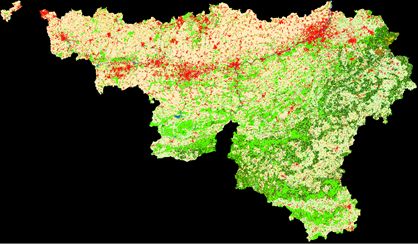
To share this experience with the biodiversity community and to help biodiversity research, the LW-WB team launched a webGIS, where thematic information derived from remote sensing data is combined with integrated abiotic variables provided in numeric fields. The spatial unit to compute the variables is the ecotope, a small polygon with largely homogeneous ecological functions. Those ecotopes are derived from homogeneous patches of land cover and topography.
The data are currently covering the Walloon Region.
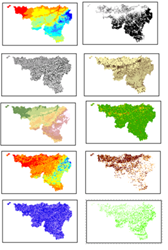
For a download of the data and a description of the currently existing fields, click on the link below.
To share this experience with the biodiversity community and to help biodiversity research, the LW-WB team launched a webGIS, where thematic information derived from remote sensing data is combined with integrated abiotic variables provided in numeric fields. The spatial unit to compute the variables is the ecotope, a small polygon with largely homogeneous ecological functions. Those ecotopes are derived from homogeneous patches of land cover and topography.
The data are currently covering the Walloon Region.


For a download of the data and a description of the currently existing fields, click on the link below.